
Our Office
3125 Coffee Rd.
Suite 1
Modesto, CA 95355
Existing Patients: (209) 529-2726
New Patients: (209) 207-5740
Visit Us Online

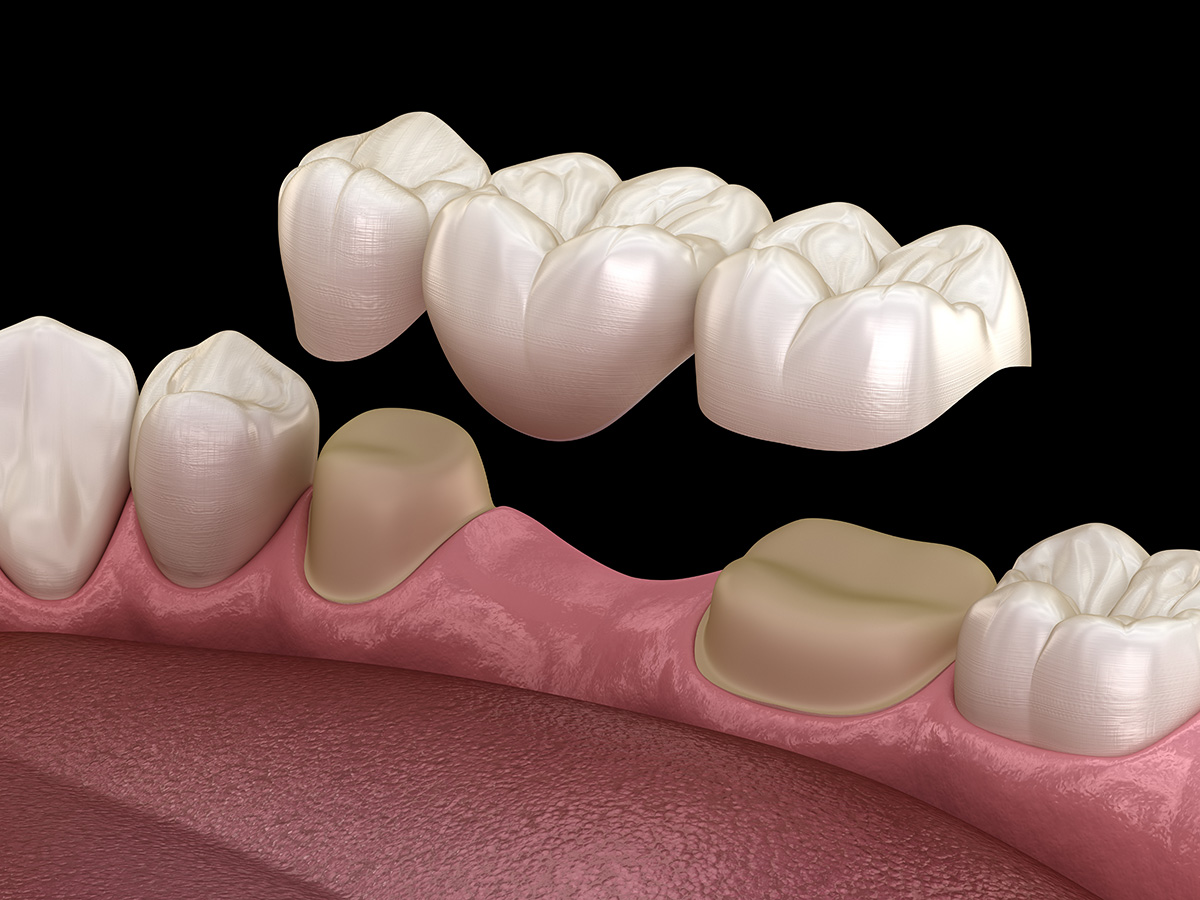
A dental bridge is a fixed restoration that replaces one or more missing teeth. The bridge is anchored by attaching to adjacent teeth or dental implants. The false tooth is called a pontic; the bridge consists of two or more crowns for the anchoring teeth and a false tooth in between. At Wayne T. Yee, DDS, replacing missing teeth with a dental bridge restores your smile’s appearance and prevents your remaining teeth from shifting into space. It also improves your ability to chew and speak properly.
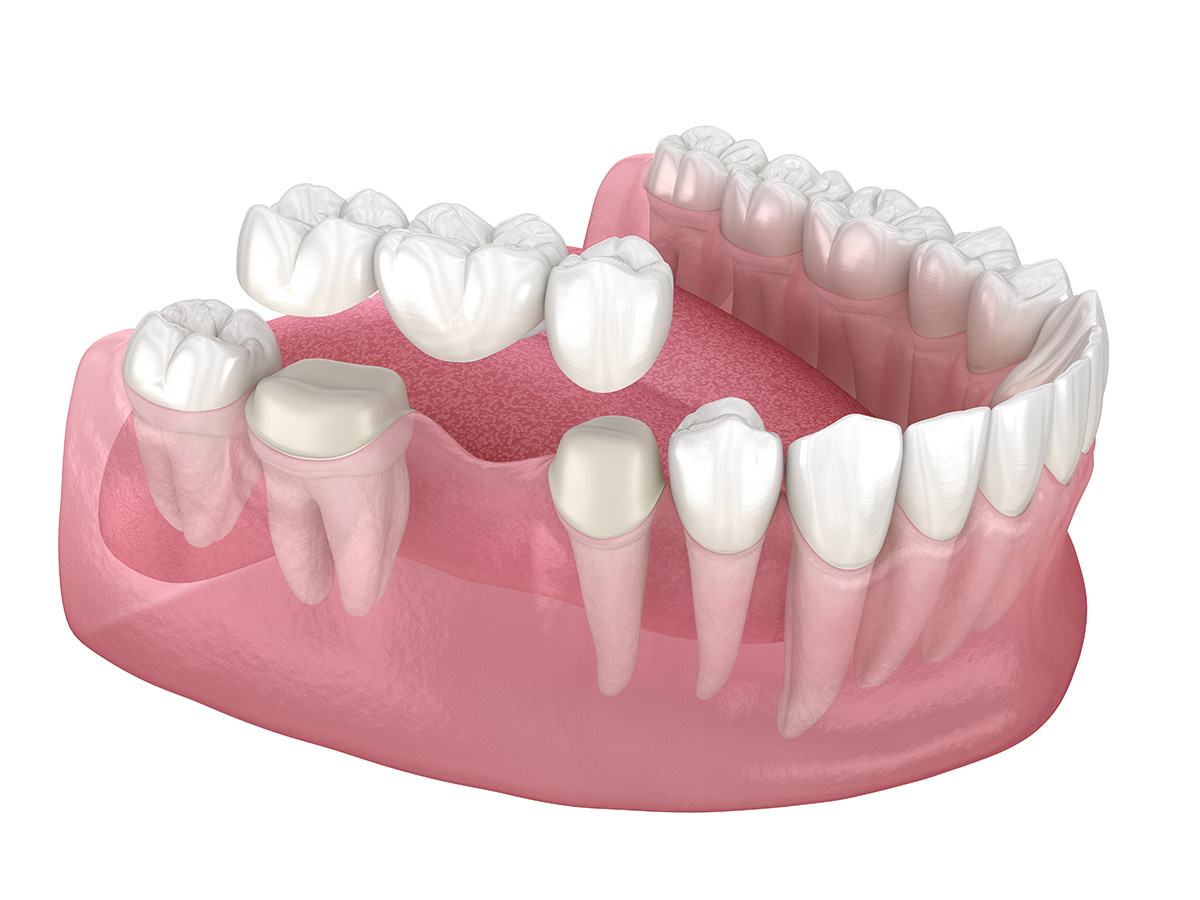
The most common type of dental bridge is a traditional bridge. This bridge consists of a false tooth suspended between two dental crowns. These crowns are cemented to the teeth on either side of the gap left by the missing tooth.
This type of bridge is used when there is only one natural tooth next to the missing tooth or teeth. The anchor tooth or teeth is prepared in the same way as for a traditional bridge. However, the pontic is not held in place by a crown; instead, it is attached by a wing on one side of the abutment.
The Maryland bridges are similar to traditional bridges, except they use a metal framework instead of crowns. The metal wings are attached to the backs of the teeth adjacent to the gap, and the false tooth is attached to these wings.
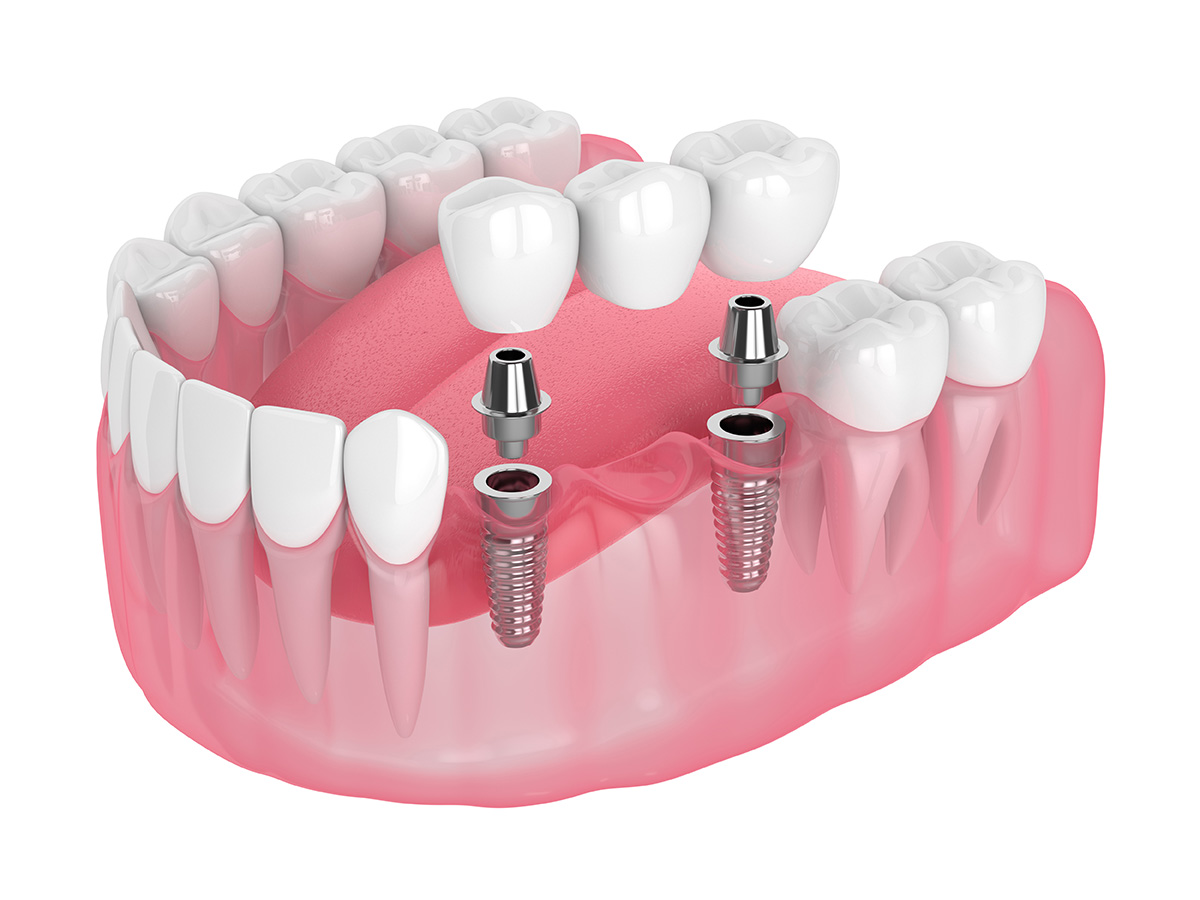
An implant-supported bridge is a permanent solution that uses dental implants as anchors instead of natural teeth. This option requires surgery to place the implants.
Brushing twice daily and flossing once daily are the best ways to keep your bridge clean. Flossing is essential because food particles can become trapped under the bridge and cause decay. Be sure to floss carefully around the bridge to remove debris from underneath.
You should also avoid biting down on hard foods with your bridge. Chewing on hard candy, ice, or other hard objects can damage the cement holding the bridge in place. If you grind your teeth at night, ask your dentist about a mouth guard to protect your bridge.
Dental bridges are an excellent restorative dental solution that can transform your smile and improve oral health. Whether you have one missing tooth or several, dental bridges, offer numerous advantages, from restored functionality and improved aesthetics to preventing teeth shifting and preserving facial structure. If you have missing teeth and want a reliable and long-lasting solution, contact Wayne T. Yee, DDS, at 3125 Coffee Rd # 1, Modesto, CA 95355, or call (209) 529-2726.
A dental bridge is a fixed prosthetic designed to replace one or more missing teeth by spanning the gap and restoring normal chewing and speech. The restoration typically includes one or more false teeth called pontics held in place by crowns or other connectors attached to adjacent teeth or to dental implants. By closing the space left by missing teeth, a bridge helps prevent neighboring teeth from drifting and supports facial contours.
The bridge transfers chewing forces to the supporting abutments so proper planning and fit are essential for long-term success. Fabrication usually involves shaping the supporting teeth or placing implants, taking impressions, and fitting a temporary restoration while the final bridge is made. Final adjustment and cementation are performed when the dentist confirms a comfortable bite and proper fit.
Common bridge designs include traditional bridges, cantilever bridges, Maryland (resin-bonded) bridges, and implant-supported bridges, and each is selected based on clinical needs. A traditional bridge uses crowns on both sides of the gap to anchor the pontic, while a cantilever bridge is supported by a crown on only one adjacent tooth. Maryland bridges use a metal or ceramic framework bonded to the backs of adjacent teeth, and implant-supported bridges rely on dental implants rather than natural teeth for support.
Material choices such as all-ceramic, porcelain-fused-to-metal, or metal frameworks affect strength and esthetics and guide the selection for front versus back teeth. Your dentist will evaluate the condition of neighboring teeth, bite forces, and esthetic goals to recommend the most suitable design and materials. The implant-supported option is often favored when preserving adjacent tooth structure or when long-term bone support is a priority.
Good candidates for a dental bridge generally have one or more missing teeth with healthy adjacent teeth or adequate bone for implants, and they are committed to maintaining oral hygiene. Patients with significant gum disease or uncontrolled medical conditions such as unmanaged diabetes may require treatment or medical clearance before restorative work. In some cases, a dental implant may be recommended instead if preserving adjacent teeth is a priority or if the supporting teeth are not suitable for crowns.
A thorough evaluation including a clinical exam and radiographs helps determine candidacy and whether preparatory treatments such as periodontal therapy or root canal treatment are needed. Your dental team will review your medical history, discuss functional and cosmetic goals, and explain the advantages and limitations of bridge options. Shared decision-making ensures the selected approach matches your oral health needs and lifestyle.
Placement of a traditional fixed bridge typically requires two to three visits: initial preparation and impressions, a try-in or adjustment appointment, and final cementation. During the first visit the dentist reshapes the abutment teeth to receive crowns and takes precise impressions that the lab uses to fabricate the prosthesis, then fits a temporary bridge to protect the prepared teeth. At subsequent visits the permanent bridge is checked for fit, occlusion, and esthetics before being permanently cemented.
When an implant-supported bridge is planned, the timeline is longer because implants must be surgically placed and allowed to integrate with the bone, which can take several months. After implant healing, an abutment is attached and the bridge is fabricated and fitted in a similar way to a traditional bridge. Your dentist will outline the expected number of visits and the sequence of steps based on the chosen design and any additional treatments required.
Daily care for a dental bridge includes brushing twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste and cleaning around the abutment teeth and pontic thoroughly to remove plaque and food debris. Flossing under the pontic is critical and can be accomplished with a floss threader, interdental brush, or water flosser to prevent decay and gum inflammation beneath the restoration. Avoiding excessive force from biting hard objects and maintaining a balanced diet help protect the bridge and supporting teeth.
Nighttime habits such as wearing a custom mouthguard can protect the bridge from damage if you grind or clench your teeth. Regular professional cleanings and examination appointments allow the dentist to monitor the integrity of the bridge and the health of surrounding tissues. Promptly report any looseness, persistent sensitivity, or changes in bite so they can be evaluated before small problems become major issues.
The lifespan of a dental bridge varies with factors such as material choice, oral hygiene, bite forces, and the health of the supporting teeth or implants, and many bridges provide reliable service for several years. Excellent daily care, avoidance of damaging habits, and routine dental visits help extend the functional life of a bridge and reduce the risk of decay or periodontal problems that could compromise abutment teeth. When an implant supports the bridge, longevity benefits from the stability of osseointegration and good maintenance of the surrounding tissues.
Over time a bridge may require repair, re-cementation, or replacement due to normal wear, recurrent decay on abutment teeth, or changes in the mouth that affect fit and occlusion. Your dentist will monitor the restoration during recall visits and recommend the appropriate action if signs of wear or failure appear. Proactive care and early intervention can often preserve the restoration or make replacement more straightforward.
Potential risks include decay of the abutment teeth, sensitivity after tooth preparation, gum inflammation around the restoration, and, in some cases, fracture or debonding of the bridge. If supporting teeth are weakened or if oral hygiene is inadequate, those teeth may be more vulnerable to problems that could jeopardize the bridge. For implant-supported bridges, surgical risks include infection, implant failure, and the need for additional procedures if bone volume is insufficient.
Many complications can be minimized through careful case selection, meticulous tooth preparation, precise laboratory fabrication, and patient adherence to hygiene and follow-up recommendations. The dental team will explain specific risks related to your situation and provide instructions to reduce the likelihood of complications. Early reporting of discomfort, mobility, or changes in the surrounding gum tissue allows timely management and better outcomes.
Dental bridges, dental implants, and removable partial dentures are all valid options for replacing missing teeth, and each has distinct advantages and trade-offs depending on clinical circumstances. Traditional bridges are fixed and restore function quickly but require alteration of adjacent teeth, whereas implants replace missing teeth without affecting neighboring teeth and help preserve underlying bone. Removable partial dentures are typically less invasive initially and can be a good interim or cost-conscious solution, but they are not fixed and may feel less stable.
The best choice depends on factors such as the health of adjacent teeth, available jawbone, long-term maintenance expectations, and personal preferences regarding fixed versus removable solutions. A thorough evaluation by your dentist will compare the durability, esthetics, functional outcomes, and care requirements of each option. Together you can weigh these considerations to select the treatment that best fits your oral health goals.
Immediately after bridge placement you may experience mild sensitivity, soreness of the gums, or transient changes in bite that typically subside within a few days to weeks. Following the dentist's instructions about chewing carefully on the temporary or new restoration and avoiding very hard foods during the initial period will help ensure a smooth recovery. Pain or sensitivity that persists or worsens should be reported so the dentist can determine if an adjustment or additional treatment is needed.
Follow-up visits allow the dentist to check fit, occlusion, and tissue health and to perform any adjustments for comfort and function. Routine dental cleanings and examinations are important to maintain the health of the surrounding teeth and gums and to identify early signs of problems. Maintaining consistent home care and attending scheduled appointments helps protect the investment in the restoration and supports oral health over the long term.
During a consultation your dentist will perform a comprehensive exam, review radiographs or scans, discuss your goals and concerns, and outline appropriate bridge options tailored to your clinical needs. This visit is an opportunity to ask about the benefits and limitations of each design, what to expect during treatment, and any preparatory care that may be recommended to optimize outcomes. The dental team will provide a personalized treatment plan that explains the sequence of care and expected timelines.
To schedule a consultation at the office of Wayne T. Yee, DDS, call (209) 529-2726 or visit the practice at 3125 Coffee Rd., Suite 1, Modesto, CA 95355 to arrange an appointment. Staff can help coordinate imaging, explain necessary forms, and confirm any medical information needed before your visit. If you have concerns about oral health conditions or need to prioritize specific functional or esthetic goals, mention these when you call so the team can prepare accordingly.
